- IAM = Identity and Access Management.
- Root account is created by default.
- Users can be grouped.
- Groups only contains users and not other groups.
- User does not have to belong to a group and user can belong to multiple groups.
- Users or Groups can be assigned policies.
- Policies define permissions of the users.
Policy Structure
- Version
- Id
- Statement (one or more)
Statement
- Sid
- Effect (Allow or Deny)
- Principal (Account/User/Role) to which the policy is applied
- Action
- Resource
- Condition
Password Policy
- Minimum length
- Specific character types
- Allow all IAM to change their own passwords
- Password expiration
- Prevent password re-use
MFA
- Password you know + security device you own
- Virtual MFA device
- Physical Security Key
- Hardware Key Fob
IAM Roles for Services
- We assign permission to AWS services with IAM roles to perform actions on your behalf.
- Common Roles:
- EC2 Instance Roles
- Lambda Function Roles
IAM Credentials Report (account-level)
- Report to list all the account's users and status of their credentials.
IAM Access Advisor (user-level)
- Access Advisor shows the permissions granted to a user and when those services were last accessed.
IAM Guidelines and Best Practice
- Dont use the root account.
- Assign users to groups and assign permissions to groups.
- Strong password policy and Multi Factor Authentication.
- Roles for AWS services.
- Access Keys for CLI and SDK.
- Audit permissions using IAM Credentials Report and IAM Access Advisor.
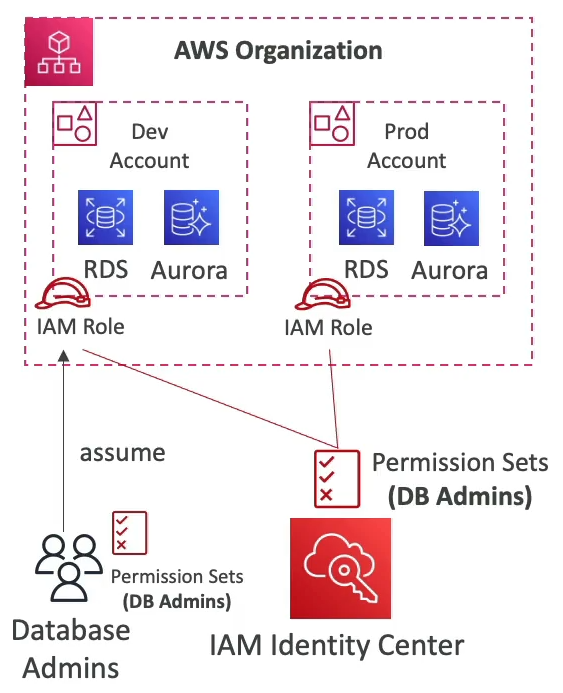
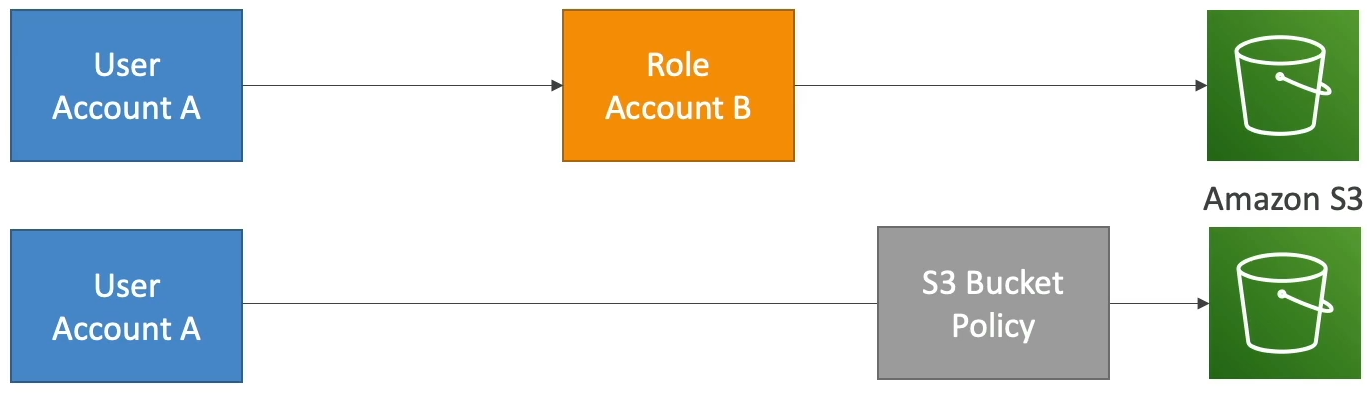
Roles and Resource Based Policies
Cross Account
- Attach a resource-based policy OR use a role as a proxy.
- When user assumes a role, it gives up original permissions.
IAM Permission Boundries
- Supported for users and roles.
- Feature to use a managed policy to set a max permissions an IAM entity can get.
AWS IAM Identity Center
- One login for all: AWS Accounts in organizations, cloud apps, etc.
Fine-grained Permissions and Assignments