On this page
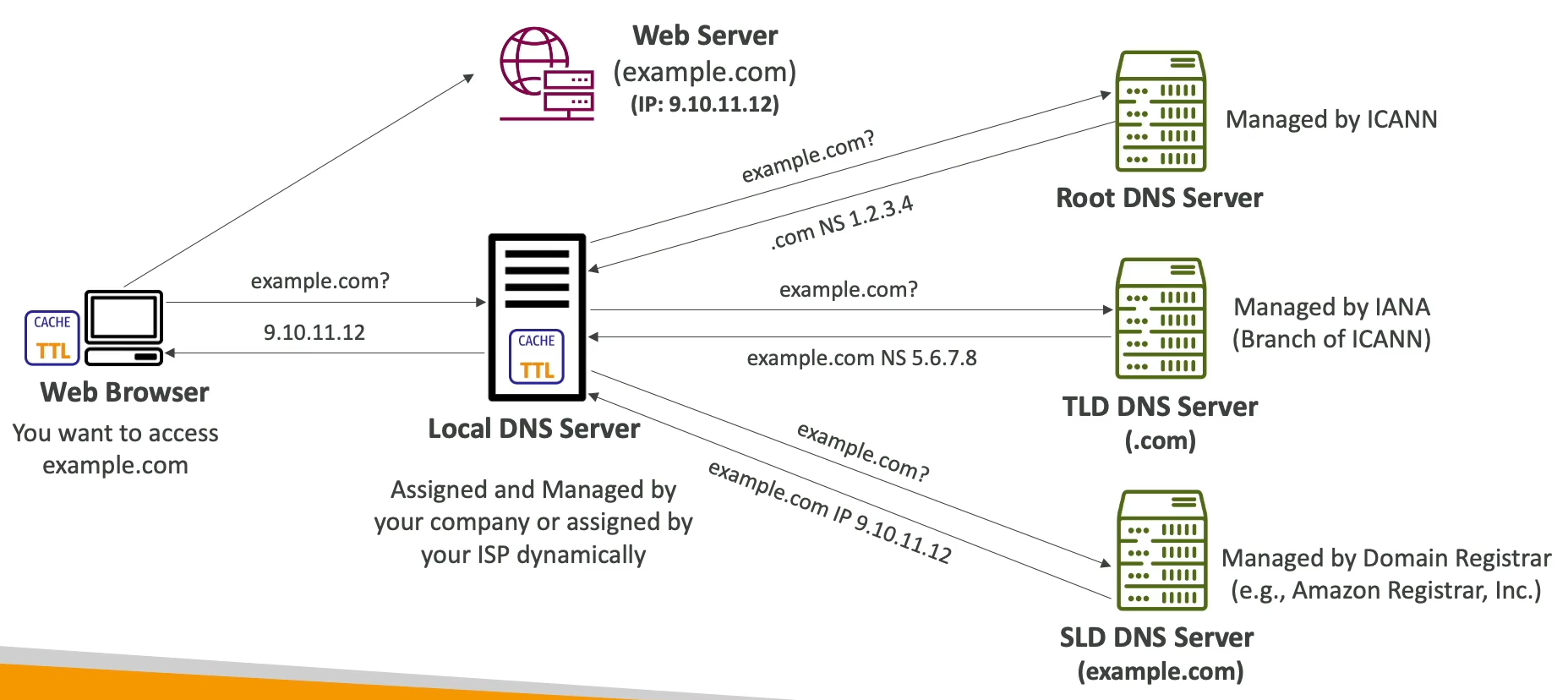
How DNS Works?
Route 53
Domain Registrar
100% availability SLA
Records
Each record contains
Domain/Subdomain Name
Record Type: A/AAAA
Value: [IP]
Routing Policy
TTL
Record Types
A: maps hostname to IPv4
AAAA: maps hostname to IPv6
CNAME: maps hostname to another hostname
NS: Name Servers
Hosted Zones
Container for records on how to route traffic to a domain/subdomain.
Public Hosted Zones : route traffic on internetPrivate Hosted Zones : route traffic within one or more VPC.
Records TTL (Time to Live)
High TTL: Less traffic on Route 53; outdated record.
Low TTL: More traffic on Route 53; easy to change records
CNAME vs Alias
CNAME: Points a hostname to another hostname; Only for non root domain.
Alias: Points a hostname to an AWS Resource; Cannot set Alias for EC2 DNS name.
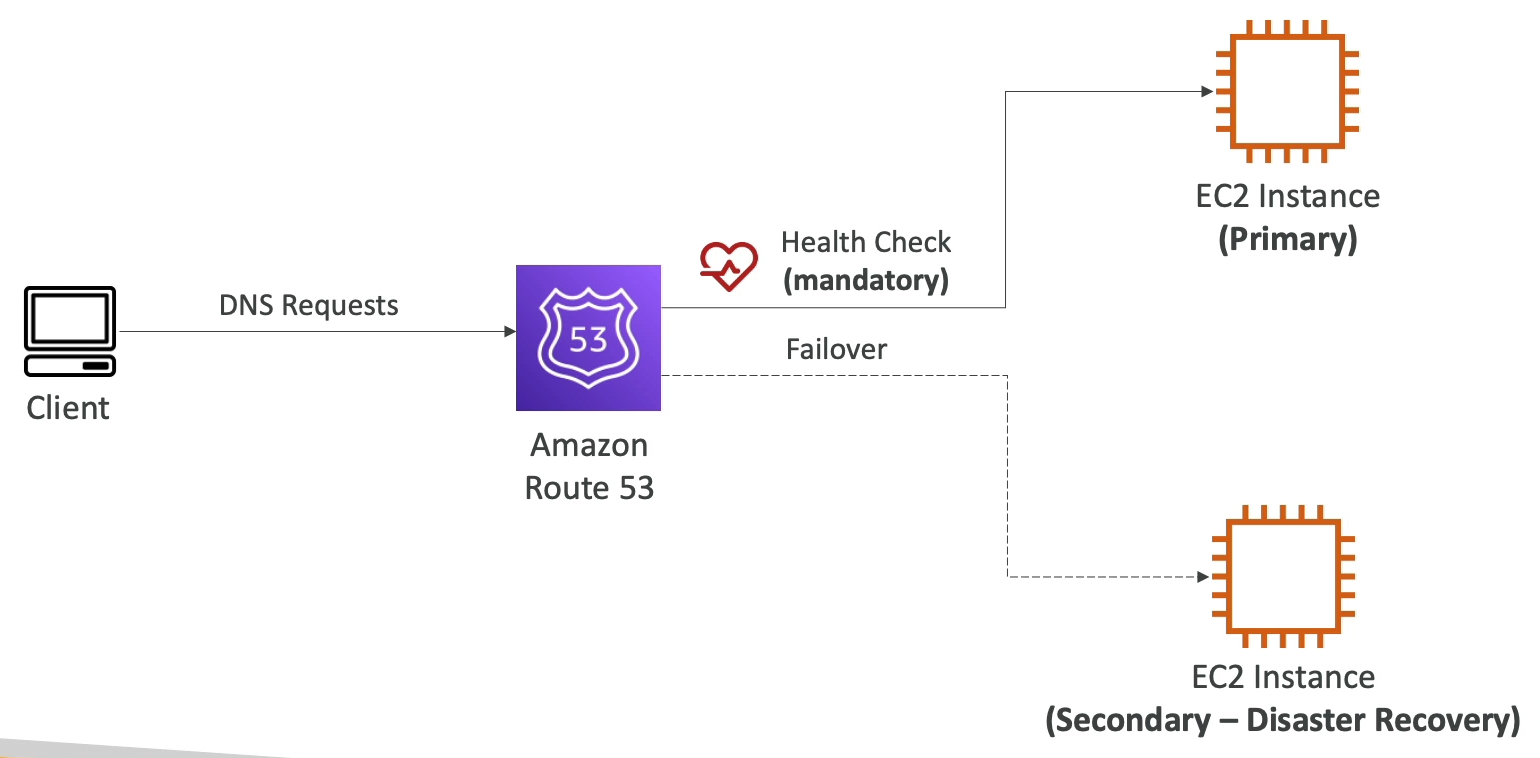
Health Checks
HTTP health checks are only for public resources.
For Private Hosted Zones, you can create a CloudWatch Metric and associate a CloudWatch Alarm, then create a health check that checks the alarm itself.
Routing Policies
Simple
Route traffic to a single resource.
If multiple values are returned, a random one is chosen.
Weighted
Control the percentage of requests that go to each specific resource.
If all the records have the weight of 0, then all the records will be returned equally.
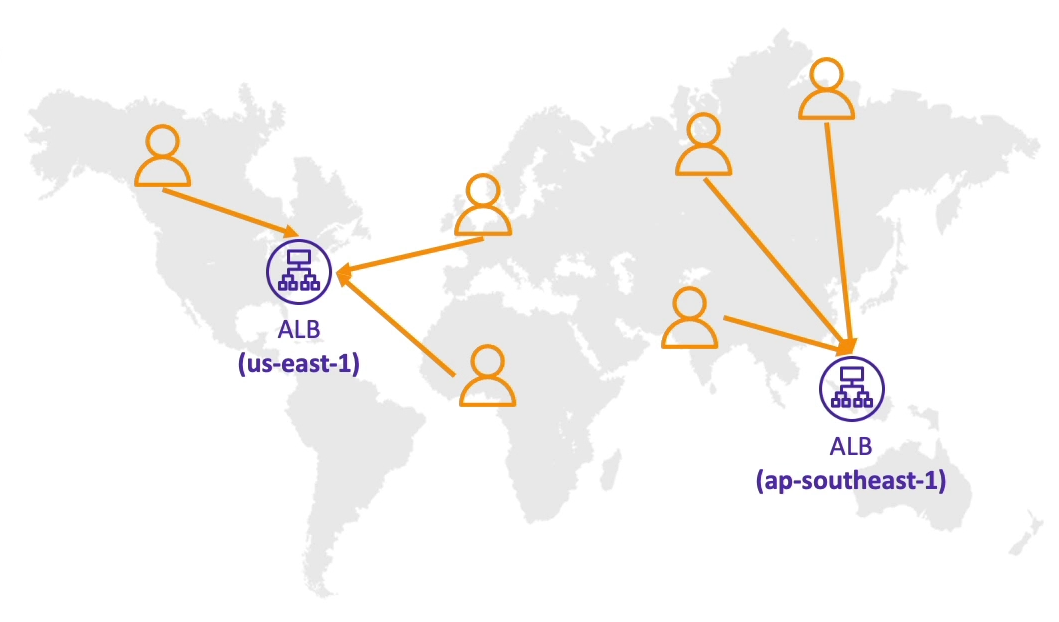
Latency-based
Redirect to the resource that has the least latency close to the user.
Failover
Geolocation
Based on user's location by continent, country, or by US State.
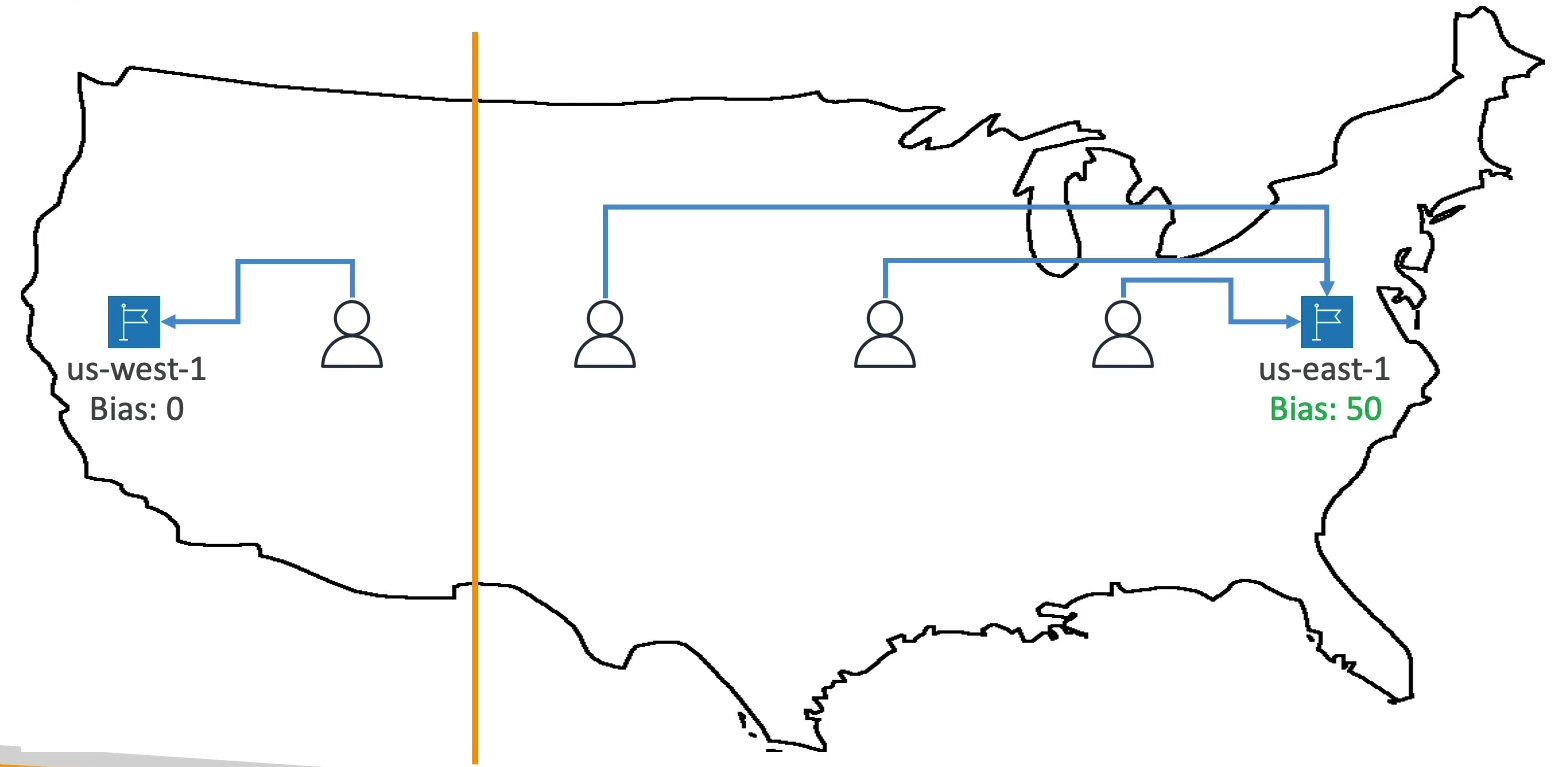
Geoproximity
Route traffic to your resources based on the geographic location of users and resources.
Ability to shift more traffic to resources based on the defined bias.
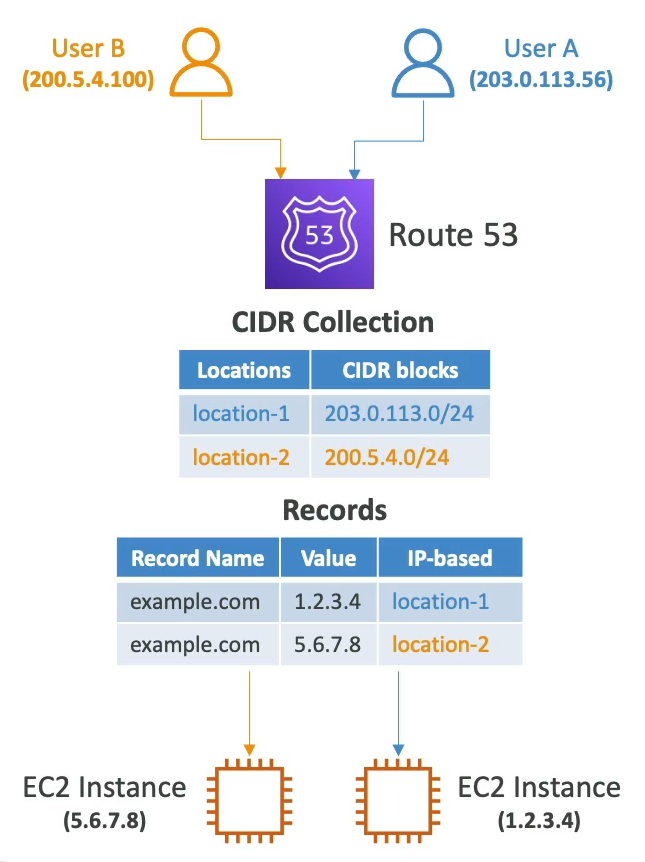
IP-based Routing
Multi-Value
Route 53 return multiple values/resources.
Can be associated with health checks (return only values for healthy resources)
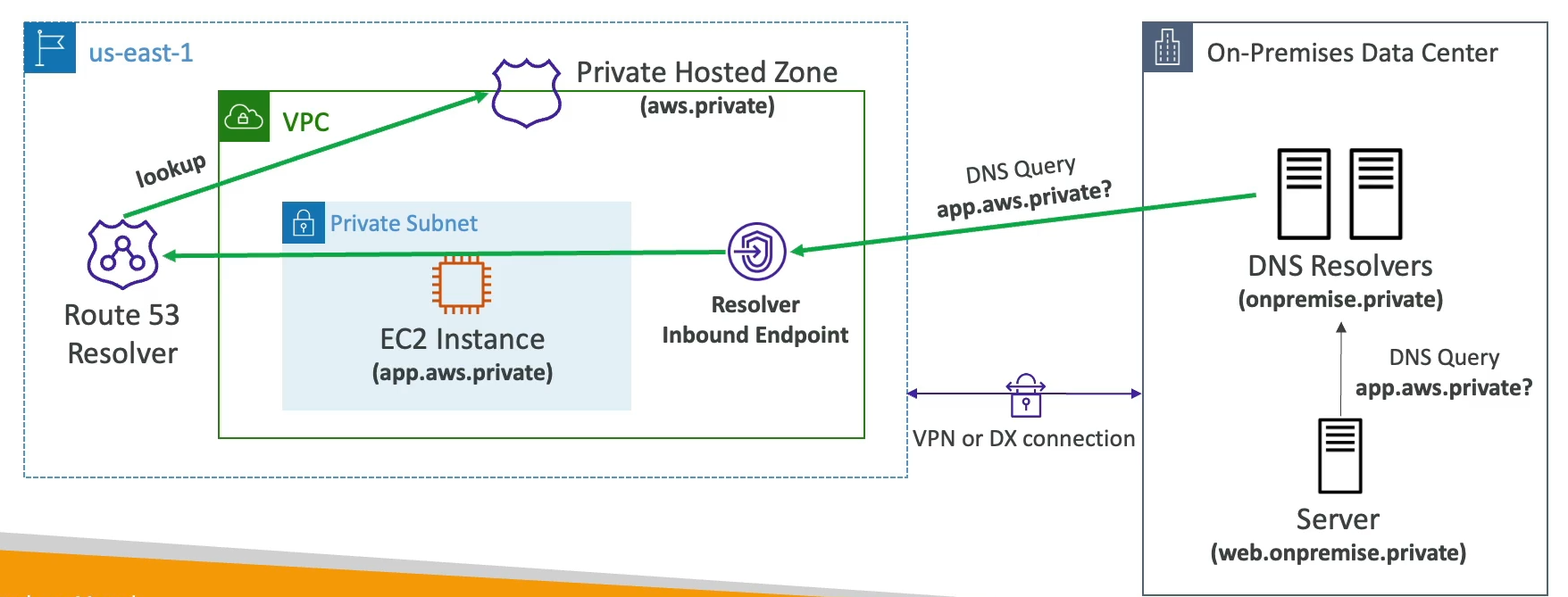
Hybrid DNS
By default Route 53 resolver answers DNS queries
Hybrid DNS: resolving DNS queries between VPC and your networks.